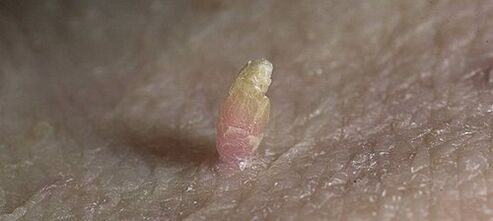
There can be a large number of diseases caused by the human papillomavirus. Furthermore, several types of this pathogen can cause the same pathology. The papilloma virus in the penis usually affects the mucous membranes and skin of the male body, localizing to the external genitalia.
A papilloma is a benign neoplasm, usually small in size, similar to a cauliflower. This oncological process develops from flat epithelial cells. The tumor appears above the skin and may have a fleshy color and a few others (white, dark brown, and so on). The causative agent of all variants of oncology is the human papillomavirus.
HPV is a DNA-containing virus and has tropism for epithelial tissues, therefore, it only affects the skin and mucous membranes of the human body. The pathogen has no shell, but is highly resistant to environmental conditions. HPV is a large group of viruses, which are subdivided into:
- Types with minimal risk of malignancy;
- Types with medium risk of malignancy (requires special conditions);
- The type with a high risk of malignant transformation.
Papillomas on the glans penis are considered a precancerous condition, meaning they belong to the last group of viruses. Therefore, at the first signs of the onset of the pathology, you should consult a doctor and start treatment. If the malignancy process has already started, therapy becomes very difficult.
Reasons for Appearance
For the appearance of papilloma in the penis in men, direct contact with an infected person is necessary. Microscopic or obvious skin damage is considered a particularly important predisposing factor. The main route of transmission of the disease is sexual. Furthermore, not only people with papillomas with a clear clinical picture are infected, but also latent carriers of the virus. During traditional sex, the head of the penis is affected, during oro-genital contacts - the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx, during anal - the anus and rectum.
If a man has HPV elsewhere, during shaving and other manipulations associated with injuries, papillomas may appear on the skin of the penis. The household route of infection is also possible, which is associated with the high resistance of the virus to environmental conditions. Baths and saunas are especially dangerous.
Predisposing factors for the manifestation of the disease:
- Decrease in the body's immunological strength;
- Prolonged stress;
- The presence of chronic diseases;
- Excessive ultraviolet radiation;
- Taking certain medications.
Clinical condition
The incubation period for papilloma in the skin of the penis is approximately 8-12 weeks, but it can vary a lot, as the clinical picture depends mainly on the degree of protection of the body.
Although HPV most often causes harmless pathologies that do not cause inconvenience to patients, the types of virus that cause the appearance of papillomas in the penile region are highly oncogenic. In other words, the appearance of neoplasms can be considered the first stage of the cancer process.
Papillomas in the penis look like small skin-colored neoplasms, single or multiple, not accompanied by subjective symptoms. Sometimes they can look like cauliflower, sometimes they are a swelling on the stem. In the absence of adequate treatment, the disease progresses and the following phases are distinguished in it:
- Phimosis (narrowing of the foreskin blades, which makes it impossible to remove the glans penis);
- The accumulation of smegma and, consequently, the development of the infectious process (due to the narrowing, it is difficult to clear the space between the head and the leaves of the foreskin);
- Inflammation of the head of the penis and both leaves of the foreskin (local signs are expressed as edema, redness, purulent discharge);
- Erosive defects in the head of the penis and foreskin (this condition is defined as the first stage of cancer).
Treatment of penile papillomas must be immediate and radical in order to avoid dangerous complications that can lead to a significant interruption of life or even death.
Diagnosis
Removal of papillomas in the penis can only be planned after the diagnosis is finally established. The main diagnostic measures for this disease:
- Complaints evaluation, clinical history and clinical picture. The presence of unprotected intercourse is clarified, the affected area is examined for the presence of cauliflower-like skin color growths. It is also possible to detect these formations in the mucous membranes of the mouth, around the anus, and in other external genital organs, except the penis.
- Polymerase chain reaction. This technique is difficult to implement, but more than 95% effective, which is why it is considered the gold standard. With the help of PCR, it is possible to detect the DNA of the virus in the human body, as well as accurately determine its type.
- Cytological studies. Through different techniques, antibodies against HPV are detected, which allows to assess the presence of an infection.
Treatment of penile papillomas is carried out immediately after the exact determination of the HPV type and stage of development of the disease.
How to get rid of papillomas on the penis?
There are no effective types of conservative treatment for this infection. The only possible action is the radical removal of the papillomas from the penis. Several techniques are used for therapy:
- Laser removal;
- Cryosurgery;
- Radio wave method (the most ideal option, leaving no cosmetic defects, painless);
- Open surgery;
- Cauterization (chemical agents are used).
Medications can be used in addition to radical therapy. Basically, preference is given to cytostatic drugs. Also, antiviral medications are prescribed to reduce the risk of relapse.
During the treatment period, sexual intercourse should be avoided to prevent the spread of infection. It is also recommended that all of the patient's sexual partners be tested for the presence of HPV.
Prophylaxis
Preventive measures mainly consist of introducing a protected sex life with a proven partner. Great care must be taken when visiting public baths and saunas, as well as avoiding contact with any neoplasms in a person, especially in the presence of microtrauma.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to consult a physician in a timely manner and to follow all his or her consultations and recommendations.
Curing the symptoms of the disease, unfortunately, does not guarantee the patient's complete recovery (ie, if the penile papilloma is removed, it will still not work to remove the virus from the body), so the man must be careful to monitor his condition, observing minor changes and referring them to a doctor. The HPV carrier must maintain a high level of immunity so that clinical manifestations (recurrence) do not occur again.














































































